Welcome To Kidney Treatment By N.D Ayurvedic & Panchkarma Centre
Send Your Query or Call at our Renal Helpline (+91)-7791006006
KIDNEY STONES/RENAL CALCULI
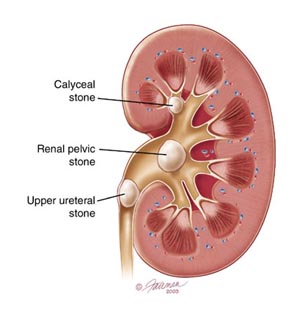
A kidney stone, also known as a renal calculus (from the Latin ren, "kidney" and calculus, "pebble") is a solid concretion or crystal aggregation formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals in the urine. Urinary stones are typically classified by their location in the kidney (nephrolithiasis), ureter (ureterolithiasis), or bladder (cystolithiasis), or by their chemical composition (calcium-containing, struvite, uric acid, or other compounds). Kidney stones are a significant source of morbidity. 80% of those with kidney stones are men. Men most commonly experience their first episode between age 30–40 years, while for women the age at first presentation is somewhat later.
Kidney stones typically leave the body by passage in the urine stream, and many stones are formed and passed without causing symptoms. If stones grow to sufficient size (usually at least 3 millimeters (0.12 in)) they can cause obstruction of the ureter. Ureteral obstruction causes postrenal azotemia andhydronephrosis (distension and dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces), as well as spasm of the ureter. This leads to pain, most commonly felt in the flank(the area between the ribs and hip), lower abdomen and groin (a condition called renal colic). Renal colic can be associated with nausea, vomiting, fever,blood in the urine, pus in the urine, and painful urination. Renal colic typically comes in waves lasting 20 – 60 minutes, beginning in the flank or lower back and often radiating to the groin or genitals. The diagnosis of kidney stones is made on the basis of information obtained from the history, physical examination, urinalysis, and radiographic studies. Ultrasound examination and blood tests may also aid in the diagnosis.
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
The hallmark of stones that obstruct the ureter or renal pelvis is excruciating intermittent pain that radiates from the flank to the groin or to the genital area and inner thigh. This particular type of pain, known as renal colic, is often described as one of the strongest pain sensations known. Renal colic caused by kidney stones is commonly accompanied by urinary urgency, restlessness, blood in the urine, sweating, nausea and vomiting. It typically comes in waves lasting 20-60 minutes caused by peristaltic contractions of the ureter as it attempts to expel the stone. The embryological link between the urinary tract, the genital system and the gastrointestinal tract is the basis of the radiation of pain to the gonads, as well as the nausea and vomiting that are also common inurolithiasis.Postrenal azotemia and hydronephrosis can be observed following the obstruction of urine flow through one or both ureters.
CAUSES
Dietary factors that increase the risk of stone formation include low fluid intake, and high dietary intake of animal protein, sodium, refined sugars, fructose andhigh fructose corn syrup, oxalate, grapefruit juice, apple juice, and cola drinks.
AYURVEDIC TREATMENT
Ayurvedic treatment has been very famous in the treatment f kidney stone since ages and the results are really encouraging . For a stone which is painful ayurvedic formulations give very quick removal and the approximate time depends upon the location of the stone and the size of the stone.
The following time periods have been calculated as per our experience:
The following time periods have been calculated as per our experience:
| SIZE OF STONE | TIME PERIOD (APPROXIMATE) |
|---|---|
| Below 5 mm | 10 days |
| Below 10 mm | 1 month |
| Below 15 mm | 2 months |
| Below 20 mm | 3 months |
| Above 20mm | 6 months |
Kidney Treatment
100% Ayurvedic treatment for kidney failure.ND Ayurveda provides research based treatment for all type Kidney Diseases.
Get Kidney Treatment Now
Call Us: (+91)-7791006006
Call Us: (+91)-7791006006
Ayurvedic Kidney Care